Decadent Delights: Exploring the Irresistible World of Chocolate and Its Surprising Health Benefits
Indulging in chocolate is often seen as a guilty pleasure, but what if we told you that this decadent delight comes with surprising health benefits? From rich, dark bars to creamy truffles, chocolate has captivated our taste buds for centuries, evolving into a beloved treat across cultures. However, beyond its luxurious taste, science has unveiled a world of antioxidants and mood-enhancing properties hidden within this sweet indulgence. Join us as we embark on a delectable journey exploring the irresistible world of chocolate, where each bite not only tantalizes your senses but may also contribute to your well-being. Prepare to discover how this cherished confection can be both a delightful treat and a surprising ally in your quest for a healthier lifestyle. Whether you're a chocolate connoisseur or simply looking to enjoy a sweet escape, you’ll find that the allure of chocolate extends far beyond its decadent surface.
The History of Chocolate: From Ancient Civilizations to Modern Treats
Chocolate’s journey from ancient civilizations to the modern era is a fascinating tale that spans thousands of years and numerous cultures. It all began in the tropical rainforests of Central and South America, where the cacao tree, the source of chocolate, thrived. The earliest known use of cacao dates back to the ancient Olmecs, who inhabited present-day Mexico around 1500 BC. They were the first to cultivate the cacao plant and use its beans to create a bitter, frothy beverage that was likely reserved for ceremonial and medicinal purposes. This early form of chocolate was far from the sweet treat we enjoy today, but it laid the foundation for chocolate’s enduring legacy.
The Maya civilization, which flourished from around 250 AD to 900 AD, further developed the use of cacao. They revered the cacao tree, calling it the "food of the gods." For the Maya, chocolate was a central part of their culture and daily life. They consumed it as a beverage, often mixed with spices, chili peppers, and cornmeal. It was also used in religious rituals and as a form of currency. The Aztecs, who later rose to prominence in the region, continued and expanded upon the Maya’s chocolate traditions. They believed that cacao was a gift from the god Quetzalcoatl and used it in various aspects of their society, including religious ceremonies, trade, and as a luxury item for the elite.
The arrival of European explorers in the Americas in the late 15th and early 16th centuries marked the beginning of chocolate’s introduction to the rest of the world. When Spanish conquerors encountered the Aztecs, they were intrigued by their chocolate drink, known as "xocoatl." The Spaniards brought cacao beans back to Europe, where it quickly gained popularity among the aristocracy. Over time, the preparation of chocolate evolved, with the addition of sugar and other ingredients to create a sweeter, more palatable version. By the 19th century, advancements in processing and manufacturing techniques led to the creation of solid chocolate bars and confections, making chocolate more accessible to the masses. Today, chocolate is a beloved global treat, enjoyed in countless forms and flavors.
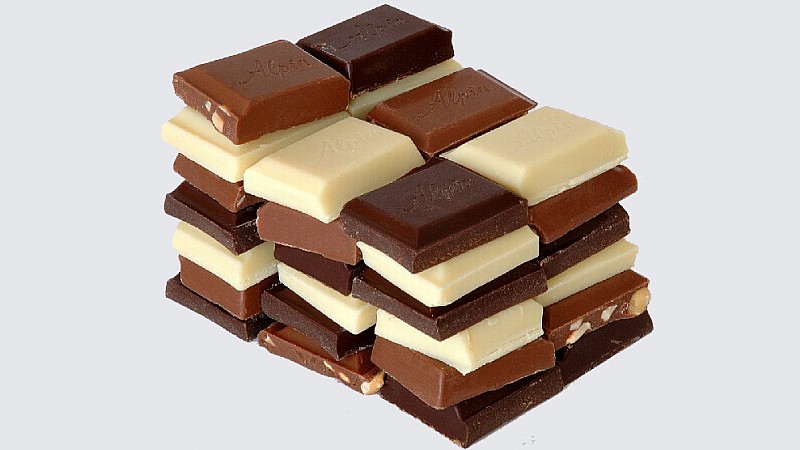
Types of Chocolate: Dark, Milk, and White - What’s the Difference?
Chocolate comes in various forms, each with its own unique characteristics and flavor profiles. The three main types of chocolate are dark, milk, and white, and they differ primarily in their ingredients and cocoa content. Understanding these differences can help you appreciate the nuances of each type and make informed choices when indulging in this delectable treat.
Dark chocolate is the purest form of chocolate, made from cocoa solids, cocoa butter, and sugar, with little to no milk solids. It has a rich, intense flavor that can range from slightly sweet to very bitter, depending on the cocoa content, which typically ranges from 70% to 100%. The higher the cocoa content, the more pronounced the chocolate’s natural flavors and the lower the sugar content. Dark chocolate is often favored by chocolate connoisseurs for its complexity and depth of flavor. It is also the type of chocolate most commonly associated with health benefits due to its high concentration of flavonoids, a type of antioxidant.
Milk chocolate, on the other hand, contains cocoa solids, cocoa butter, sugar, and milk solids, which give it a creamier, sweeter taste compared to dark chocolate. The cocoa content in milk chocolate is usually lower, ranging from 10% to 50%, resulting in a milder and more approachable flavor. The addition of milk solids not only softens the taste but also contributes to the smooth, melt-in-your-mouth texture that many people love. Milk chocolate is the most popular type of chocolate worldwide, widely used in various confections, bars, and candies.
White chocolate is quite different from both dark and milk chocolate, as it contains no cocoa solids at all. Instead, it is made from cocoa butter, sugar, and milk solids, which give it a sweet, creamy flavor and a pale ivory color. Because it lacks cocoa solids, white chocolate does not have the characteristic chocolate flavor and is often considered a confection rather than true chocolate. However, it still offers a delightful, indulgent experience, especially when paired with complementary flavors like vanilla, nuts, or fruit. While white chocolate may not provide the same health benefits as dark chocolate, it remains a beloved treat for those who enjoy its unique taste and texture.
The Science Behind Chocolate: How It Affects Your Brain and Mood
Chocolate’s allure goes beyond its delicious taste; it also has intriguing effects on the brain and mood. The science behind these effects involves a combination of chemical compounds and the pleasurable sensory experience of eating chocolate. Understanding these mechanisms can shed light on why chocolate is often considered a comfort food and a mood booster.
One of the key components of chocolate that influences the brain is theobromine, a stimulant related to caffeine. Theobromine has a milder effect than caffeine but still contributes to the feeling of alertness and energy that many people experience after consuming chocolate. In addition to theobromine, chocolate contains small amounts of caffeine, which can enhance its stimulating effects. Together, these compounds can help improve concentration and reduce fatigue, making chocolate a popular choice for a quick pick-me-up.
Chocolate also contains several compounds that can positively affect mood. One such compound is phenylethylamine (PEA), often referred to as the "love drug" because it is associated with the release of endorphins, the body's natural feel-good chemicals. PEA can create feelings of excitement and happiness, similar to the emotions experienced during romantic encounters. Another important compound in chocolate is anandamide, a neurotransmitter that binds to the same receptors in the brain as THC, the active ingredient in cannabis. Anandamide can produce a sense of euphoria and relaxation, contributing to the overall pleasurable experience of eating chocolate.
Moreover, chocolate is rich in tryptophan, an amino acid that the body uses to produce serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood and promotes feelings of well-being. Increased serotonin levels can help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety, making chocolate a natural mood enhancer. Additionally, the sensory pleasure of eating chocolate, with its smooth texture and rich flavor, can trigger the release of dopamine, another neurotransmitter associated with reward and pleasure. This combination of chemical and sensory effects helps explain why chocolate is often sought after for comfort and enjoyment.
Health Benefits of Dark Chocolate: Why It’s Good for You
While chocolate is often considered an indulgence, dark chocolate, in particular, offers a range of health benefits that can make it a guilt-free treat when consumed in moderation. These benefits are primarily attributed to its high cocoa content, which is rich in various nutrients and antioxidants. Incorporating dark chocolate into a balanced diet can contribute to overall health and well-being.
One of the most notable health benefits of dark chocolate is its positive impact on heart health. Studies have shown that the flavonoids in dark chocolate can help improve blood flow, reduce blood pressure, and decrease the risk of heart disease. These flavonoids, specifically catechins and epicatechins, help relax blood vessels and improve circulation, which can lower the strain on the heart and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. Additionally, dark chocolate can help reduce levels of LDL cholesterol, often referred to as "bad" cholesterol, while increasing levels of HDL cholesterol, or "good" cholesterol.
Dark chocolate is also a powerful source of antioxidants, which play a crucial role in protecting the body from oxidative stress and inflammation. Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body, leading to cell damage and contributing to various chronic diseases. The antioxidants in dark chocolate, including flavonoids, polyphenols, and theobromine, help neutralize free radicals and reduce inflammation, supporting overall health and longevity.
In addition to its cardiovascular benefits and antioxidant properties, dark chocolate can also support cognitive function and brain health. Research suggests that the flavonoids in dark chocolate can enhance cognitive performance, improve memory, and protect the brain from age-related decline. These benefits are thought to result from the improved blood flow to the brain and the anti-inflammatory effects of the flavonoids. Furthermore, the mood-boosting properties of dark chocolate, such as its ability to increase serotonin and dopamine levels, can help reduce stress and improve mental well-being. By incorporating dark chocolate into a balanced diet, you can enjoy its delicious taste while reaping its numerous health benefits.
The Role of Antioxidants in Chocolate: Understanding Flavonoids
Antioxidants play a vital role in maintaining health and preventing disease, and chocolate, particularly dark chocolate, is a rich source of these beneficial compounds. Among the various antioxidants found in chocolate, flavonoids are the most prominent and have been the focus of extensive research. Understanding the role of flavonoids in chocolate can help you appreciate their health benefits and make informed choices when selecting chocolate products.
Flavonoids are a group of plant-based compounds found in many fruits, vegetables, and other plant foods, including cacao beans. In chocolate, the most abundant flavonoids are catechins, epicatechins, and procyanidins. These compounds have potent antioxidant properties, meaning they can neutralize free radicals and protect cells from damage. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress, leading to inflammation and increasing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders. By combating free radicals, flavonoids help reduce oxidative stress and support overall health.
In addition to their antioxidant effects, flavonoids in chocolate have been shown to improve cardiovascular health. They do this by enhancing the function of the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels, which helps regulate blood flow and blood pressure. Flavonoids stimulate the production of nitric oxide, a molecule that relaxes blood vessels and improves circulation. This can lead to lower blood pressure, reduced risk of blood clots, and improved cardiovascular function. Studies have demonstrated that regular consumption of dark chocolate, which is high in flavonoids, can contribute to better heart health and a lower risk of cardiovascular disease.
Flavonoids also have anti-inflammatory properties, which can further support overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can contribute to various health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. The flavonoids in chocolate help modulate the body's inflammatory response, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory molecules and promoting a more balanced immune system. By incorporating flavonoid-rich dark chocolate into your diet, you can benefit from its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, supporting long-term health and well-being.
Chocolate and Heart Health: What Research Says
Chocolate, particularly dark chocolate, has been the subject of numerous studies investigating its potential benefits for heart health. The findings from this research suggest that incorporating moderate amounts of dark chocolate into a balanced diet can have a positive impact on cardiovascular health. Understanding the mechanisms behind these benefits can help you make informed choices about including chocolate in your diet.
One of the key ways dark chocolate supports heart health is by improving blood pressure. High blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke, and managing it is crucial for cardiovascular health. Studies have shown that the flavonoids in dark chocolate can help lower blood pressure by promoting the production of nitric oxide, which relaxes blood vessels and improves blood flow. This effect can lead to a reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, contributing to better overall heart health.
Another important benefit of dark chocolate for heart health is its ability to improve cholesterol levels. Cholesterol is a fatty substance that can build up in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease. Dark chocolate has been shown to reduce levels of LDL cholesterol, often referred to as "bad" cholesterol, while increasing levels of HDL cholesterol, or "good" cholesterol. The antioxidants in dark chocolate, particularly flavonoids, help prevent the oxidation of LDL cholesterol, making it less likely to adhere to the walls of the arteries and form plaques. This can reduce the risk of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the hardening and narrowing of the arteries.
In addition to lowering blood pressure and improving cholesterol levels, dark chocolate can also help reduce the risk of blood clots. Blood clots can obstruct blood flow, leading to heart attacks and strokes. The flavonoids in dark chocolate have been shown to have antiplatelet effects, meaning they can reduce the tendency of blood platelets to clump together and form clots. This anticoagulant property can help maintain healthy blood flow and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. By incorporating dark chocolate into your diet in moderation, you can enjoy its delicious taste while supporting your heart health.
The Impact of Chocolate on Stress and Anxiety Levels
Chocolate is often associated with comfort and relaxation, and for good reason. Its impact on stress and anxiety levels has been the subject of scientific research, revealing several mechanisms through which chocolate can help improve mental well-being. Understanding these effects can help you appreciate the role of chocolate as a mood-enhancing treat.
One of the primary ways chocolate helps reduce stress and anxiety is through its influence on neurotransmitters in the brain. Chocolate contains compounds such as phenylethylamine (PEA), theobromine, and anandamide, which can affect the levels of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. Serotonin is a key neurotransmitter that regulates mood, and higher levels of serotonin are associated with feelings of happiness and relaxation. By increasing the availability of serotonin, chocolate can help alleviate symptoms of stress and anxiety.
Dopamine, another neurotransmitter influenced by chocolate, plays a crucial role in the brain's reward system. The consumption of chocolate triggers the release of dopamine, creating a sense of pleasure and satisfaction. This pleasurable response can help counteract negative emotions and provide a temporary escape from stress. Additionally, the sensory experience of eating chocolate, with its rich flavor and smooth texture, can activate the brain's reward pathways, further enhancing the mood-lifting effects.
Research has also shown that the antioxidants in dark chocolate, particularly flavonoids, can have a positive impact on stress levels. Flavonoids have been found to reduce the production of cortisol, the body's primary stress hormone. Elevated cortisol levels are associated with chronic stress and anxiety, and reducing cortisol can help mitigate these effects. The anti-inflammatory properties of flavonoids also contribute to their stress-reducing benefits, as chronic inflammation is linked to increased stress and mood disorders. By incorporating dark chocolate into your diet, you can take advantage of its natural compounds to help manage stress and promote a sense of well-being.
Delicious Ways to Incorporate Chocolate into a Healthy Diet
Incorporating chocolate into a healthy diet can be both enjoyable and beneficial, especially when you choose high-quality dark chocolate with a high cocoa content. There are numerous creative and delicious ways to include chocolate in your meals and snacks without compromising your nutritional goals. Here are some ideas to get you started.
One simple and satisfying way to enjoy dark chocolate is by adding it to your breakfast. For example, you can sprinkle some chopped dark chocolate or cocoa nibs onto your morning oatmeal or yogurt. This not only adds a rich, chocolatey flavor but also provides a boost of antioxidants and nutrients. Another option is to blend a small piece of dark chocolate into your smoothie, along with fruits, vegetables, and a source of protein like Greek yogurt or protein powder. This creates a delicious, creamy beverage that satisfies your chocolate cravings while delivering essential vitamins and minerals.
Dark chocolate can also be incorporated into savory dishes for a unique and flavorful twist. One popular example is using dark chocolate in chili or mole sauce. The chocolate adds depth and complexity to the dish, balancing the heat of the spices with its rich, slightly bitter taste. You can also experiment with adding a small amount of dark chocolate to sauces, stews, or marinades to enhance the flavor profile. Pairing dark chocolate with ingredients like nuts, seeds, and dried fruits in a homemade trail mix is another healthy and convenient option for a snack that provides a balance of protein, healthy fats, and antioxidants.
For those with a sweet tooth, there are plenty of healthier dessert options that feature dark chocolate. You can make chocolate-dipped fruits, such as strawberries, bananas, or apple slices, for a nutritious and indulgent treat. Another idea is to bake with dark chocolate, using recipes that incorporate whole grains, nuts, and minimal added sugars. For example, you can make dark chocolate avocado brownies or dark chocolate chia seed pudding for a dessert that is both delicious and nutritious. By exploring these creative ways to incorporate dark chocolate into your diet, you can enjoy its many health benefits while satisfying your cravings.
Myths and Misconceptions About Chocolate and Health
Despite the growing body of evidence supporting the health benefits of chocolate, there are still several myths and misconceptions that persist. Separating fact from fiction can help you make informed decisions about including chocolate in your diet and appreciate its true potential as a healthful indulgence.
One common myth is that all chocolate is unhealthy and should be avoided. While it is true that some chocolate products, particularly those high in sugar and unhealthy fats, can contribute to weight gain and other health issues, high-quality dark chocolate with a high cocoa content can offer numerous health benefits. The key is to choose chocolate with minimal added sugars and artificial ingredients, and to enjoy it in moderation. Dark chocolate, in particular, is rich in antioxidants, flavonoids, and other nutrients that can support heart health, cognitive function, and overall well-being.
Another misconception is that chocolate causes acne and other skin problems. While it is a common belief that chocolate can lead to breakouts, research has not found a direct link between chocolate consumption and acne. In fact, the antioxidants in dark chocolate may actually benefit skin health by reducing inflammation and protecting against oxidative stress. Of course, it is important to consider individual reactions and sensitivities, as some people may experience skin issues related to certain ingredients in chocolate products, such as dairy or sugar.
There is also a myth that chocolate is highly addictive and should be avoided to prevent cravings and overeating. While chocolate does contain compounds that can trigger pleasurable responses in the brain, such as theobromine and phenylethylamine, it is not inherently addictive. Cravings for chocolate are often related to its sensory appeal and emotional associations rather than a physical dependence. By enjoying chocolate mindfully and in moderation, you can savor its delicious taste without falling into patterns of overconsumption. Understanding these myths and misconceptions can help you appreciate the true benefits of chocolate and incorporate it into a balanced, healthy diet.
Conclusion: Indulging Mindfully in the World of Chocolate
As we have explored, chocolate is not only a beloved treat but also a source of surprising health benefits. From its rich history